Chronic back pain is a serious and common affliction that impacts your mental and physical health. Each year, millions of people are affected by this irritable pain and there are plenty of causes to each case. However, one thing is for sure: according to the CDC, around 25% of Americans experience some sort of lower back pain, so you’re not alone in this.
As a result, many people seek for some relief such as painkillers, not realizing that there are much better drug-free options they can use. It’s true that painkillers offer temporary relief for your chronic back pain, but they don’t address the actual cause of the problems. That’s why it’s important you realize how common back pain is, so you raise awareness about drug-free remedies like chiropractic care.
If you’re one of those people who have experienced chronic back pain at least once in your life, this article is for you. You can learn more about the latest statistics, main causes, available treatments, and much more.
Summary of Statistics
- Chronic low back pain is the main cause of global disability.
- Back pain is one of the most common health conditions as 80% of adults experience it at least once in their life.
- Every year, 50% of working adults have reported having low back pain symptoms.
- After joint and skin disorders, low back pain is the third most common reason for visiting the doctor.
- 1 in 3 people report that back pain affects their everyday life and activities.
What are the Different Types of Back Pain?
Whether you suffer from back pain or not, it can be difficult to distinguish between the different types of back pain. That’s why we compiled a list with the most common types of back pain for better comprehension.
Acute pain: is more common and is usually caused by a fall or car accident. It lasts less than 6 weeks and it goes away along with the cause of the pain, so your life gets back to normal.
Subacute pain: lasts around 6 weeks and 3 months.
Chronic pain: is the type of pain that lasts for a long time, more than 3 months. It’s ongoing and it can cause you to experience episodes of back pain even after the cause of the problem has gone away. Sufferers can also be affected by chronic pain even when the damage or the injury is not apparent, that’s why some researchers tend to think that there might be a mind/body connection.
What are the Different Types of Low Back Pain?
Low back pain is mainly classified into 2 broad categories: mechanical and radicular.
Mechanical: is the most common cause of back pain and it usually comes from bones, muscles, joints, or ligaments.
Radicular: occurs when there’s a spinal nerve that becomes impinged or inflamed.
What are the Different Types of Back Pain Treatment?
As mentioned before, back pain is an ongoing condition that isn’t relieved by a single treatment process. However, there are some other treatment alternatives that can help alleviate back pain.
Medication
Obviously, medication is one of the most common and easiest ways to manage back pain. Over-the-counter drugs and prescription have proven to be highly effective in relieving back pain.
Additionally, painkillers are the primary treatment prescription that’s used to manage back pain, but you should know that they only work as short-term relief. According to a study by Statistica, 49% of respondents said they used painkillers, 32% rested regularly, while 30% engaged in back activities.
Chiropractic Treatment
A more conventional treatment for back pain is chiropractic. This procedure is performed by licensed and trained professionals also known as chiropractors.
The US is estimated to have more than 70,000 licensed chiropractors in the chiropractic industry.
As stated by the University of Michigan, 4 out of 10 Americans visit chiropractors, where 40% consult them for treatment, while 20% go to a subspecialist for their pain.
Physical Therapy
Another alternative to help relieve back pain is physical therapy. This approach includes manual therapy, exercises, and superficial heat. One of the biggest reasons as to why people go to physical therapy is spine pain and this treatment has received its fair share of positive and negative reviews.
Surgery
In cases of chronic back pain, surgery is recommended. The main purpose of surgery is to alleviate pain, while improving lumbar spine stability.
In the US, many people with LBP are considering surgery, though only 5% of them actually need it. In 2004, around 13 billion dollars were spent on spinal surgery.
Injections
Another relief mechanism for back pain is steroid injections. However, they only provide short-term relief, much the same like painkillers. As the American guidelines show, people who have used steroid injections may still need to undergo surgical procedures.
Acupuncture
A better option for managing your back pain than steroid injections is acupuncture. Even the US medical guidelines have approved acupuncture as a relief treatment for acute LBP.
What Causes Back Pain?
The back is complicated; it’s full of bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments. It may happen that you sprain ligaments, irritate joints, or strain muscles, and these can all lead to back pain. Although it’s common for accidents and sports injuries to cause back pain, sometimes even the simplest movements can cause immense pain in your lower back.
Not only that, but also poor posture, arthritis, psychological stress, and obesity can contribute or complicate your back pain further. In addition, back pain can also be caused from disease of internal organs like kidney infections, kidney stones, bone loss, or blood clots.
Genetic disorder: genetic disorders such as arthritis can play a huge role when it comes to back pain.
Fitness: usually, back pain is more common for people who don’t exercise often. If you exercise regularly, you are more likely to strengthen the core muscles that support the back. Even a simple walk every day can improve your spinal health.
Inactive lifestyle: apart from not exercising, having an inactive lifestyle means working on a desk job all day or sitting in uncomfortable chairs that lead to more back pain.
Smoking: interestingly enough, smoking stops oxygen flow to the spinal tissue which causes back pain.
Sudden weight gain: although obesity plays its role in back pain, rapid weight gain can also put a lot of stress on the neck and back.
Improper lifting: you should always lift with your legs, not your back. If you repeatedly do improper lifting, this will put you at a higher danger for back pain.
What are other Possible Causes of Back Pain?
Aside from the above mentioned causes, there are some other factors that may impact the severity of back pain. Below, you can also find some statistics along with other possible causes.
1. 9 out of 10 patients don’t know the cause of their lower back pain
Physically demanding and heavy activities can definitely increase the risk of lower back pain; however, there are some other issues which remain unidentifiable. That’s why it’s hard to determine the main source of pain.
2. Inactive lifestyle can cause back pain in 54% of the cases
For people who spend majority of their workdays sitting, back pain is unavoidable. Additionally, based on the findings of the University of Waterloo, standing desks aren’t as beneficial as they claim to be. Not only that, but 40% of the study’s participants (who didn’t have previous back issues) started experiencing lower back pain symptoms after sitting for two hours. That’s why it’s recommended you change your posture quite often while working on a desk.
3. Stress is the main cause of back pain for 29% of people who already deal with back problems
According to a study by Statista, almost 30% of US adults stated that stress is the cause for their back problems. At the same time, 29% also said that lack of exercise or weak muscles are the main causes of their back pain, while another 26% said that physical work has greatly influenced their back pain.
4. Gymnasts have the highest risk of developing back pain issues
Among athletes, 85% of gymnasts experience lower back pain at some point in their lives. However, weightlifting and wrestling are not too far off behind, with 80% and 69%.
5. 63% of people stated that a new mattress relieved their back pain
According to sleep.org, an uncomfortable bed leads to back pain. If you’re already suffering from back pain problems, a medium-firm or firm mattress would help relieve your backache since these will keep your spine aligned perfectly.
Low Back Pain as a Common Global Problem
It’s true, chronic low back pain remains a common global problem. Additionally, the Global Burden of Disease studies defines low back pain (LBP) as ‘’ pain in the area on the posterior aspect of the body from the lower margin of the twelfth ribs to the lower gluteal folds with or without pain referred into one or both lower limbs that lasts for at least one day”
In 2017, the point prevalence of LBP was approximately 7.5% of the global population, which is equivalent to 577.0 million people. Since 1990, LBP remains the main cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) and a global health concern.
Low Back Pain as the Leading Cause of Global Disability
Since 1990, the global burden of disability has been increasing. Disability associated with LBP has increased between the 1990 and 2019 in all age groups. Apart from that, around 70% of years lost through disability included people of ages between 20-65 years.
Chronic Low Back Pain Doesn’t Always Equal Disability
Approximately, less than 1 in 3 people living with high-impact LBP have stated they have restricted participation in work, self-care activities, and social activities for 6 or more months.
Despite the fact that fewer than 28% of people with LBP have reported severe disability, they count for 77% of every disability that’s caused by chronic low back pain.
The Prevalence of Back Pain
If you’ve ever wondered if back pain is common, here we’ll focus on the prevalence of back pain.
1. Around 80% of Americans have experienced back pain at some point in their lives
Statistics show that around 31 million American suffer from low back pain. This common chronic pain is usually caused by heavy activities such as carrying heavy loads or running. Sometimes, even the slightest movements such as bending down to tie your shoes can cause back pain.
The majority of adults have experienced back pain at some degree. According to statistics, around 27 million Americans from ages of 18 or older have reported some type of back pain.
2. 60% to 70% of people from industrialized countries have experienced chronic low back pain
According to World Health Organization (WHO) statistics, many people with low back pain have reported that this issue has affected their productivity at work, with a general negative effect on their physical well-being.
3. Around half of US workers have back pain problems each year
Majority of Americans miss work due to back pain. In fact, this issue is one of the most common causes of work absences in the US. The American Chiropractic Association reports that 264 million workdays are lost each year because of chronic low back pain.
4. Approximately 20% of people who experienced acute low back pain will also suffer from chronic pain
If your back pain lasts for at least three months, then it’s usually defined as chronic pain.
5. Episodes of LBP are common among patients
According back pain statistics, the majority of patients who have experienced an episode of acute lower back pain also have similar symptoms within two years.
Is Lower Back Pain More Common with Men or Women?
According to most recent studies, women have reported having lower back pain. According to a German study, 40% of women reported a 7-day prevalence and only 32% for men. Similarly, another study from Spain estimated that currently, low back pain is most prevalent for women (18%) and less for men (11%). Additionally, 45% of pregnant women have reported lower back pain during their pregnancy, but that could be due to the changes in their posture or hormonal imbalance.
Despite the fact that more women suffer from back pain problems, men more often report that backache impacts their productivity at work.
How common is Lower Back Pain?
- In the US alone, more than 8% of the population reports having severe lower back pain.
- Globally, back pain seems to be the main leading cause of disability.
|
Low Back Pain Type |
Population Average |
Estimated Population with Pain Average |
Prevalence |
|
Frequent, Severe Low Back Pain |
145,804,000 |
11,882,000 |
8.18% |
|
Low Back Pain Affected by Work |
145,742,000 |
8,274,000 |
5.25% |
How Many People Find Solutions?
Most back pain sufferers recover, but a small percentage experiences recurring episodes of LBP which develop a chronic problem that later turns into limited mobility and constant pain.
Fun fact: back pain is one of the most mysterious conditions because only 10% of doctor visits lead to correct diagnosis.
Is Back Pain Becoming More Common?
Undoubtedly, yes! Globally, there has been an incensement for disability caused by back pain for up 54% in the last three decades. This is mainly because of an increase in population and aging, while the biggest increases were seen in low and middle-income countries.
Low back pain is estimated to become a lot more common and prominent, increasing costs and disability, especially in low and middle-income counties that don’t have the capacities to deal with this issue.
The Costs of Back Pain
Of course, there are direct and indirect costs of back pain, but what are the exact financial repercussions of back pain? Here, we’ll discuss the economics of backaches in statistics so you get a better understanding of this issue.
Lower Back Pain is Equivalent to $100 Billion per Year
According to American Chiropractic Association, the back pain statistics show that medical care costs round up to approximately $50 billion, while decreased productivity and lost wages account the other half.
On average, the Cost for Back Treatment Rounded up to $1,500 to $1,600 per Person
Back in 2007, the cost for back treatment amounted up to $1,600 per person. In addition to that, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), 45% of medical fees are covered by private insurance, while Medicare covers 23%. At the same time, patients also have to pay around 16% of their treatment costs.
FAQs about Economics of Back Pain
Although statistics speak for themselves, there are certain questions that you might have in mind. Below, we answer some of the most common questions that people who suffer from back pain might have.
Who can help to reduce the Cost of Back Pain Treatment?
Costs can be reduced with the help of insurance. However, in other cases, 55% of the costs are reduced when people invest in physical therapy before opting for more invasive treatment alternatives.
On average, how much is spent in the US on back pain?
Annually speaking, the current estimate in the US is that $86 billion is spent on back pain.
Do increased clinical treatment alternatives improve patient outcomes for back pain?
Although it’s true that costs have increased, there is no clear evidence that back pain in patients is improved.
On average, how many days of work are lost because of back pain?
As mentioned before, back pain is one of the most common reasons for missing work. As such, there are 186.7 million days of work lost annually, all of which lead to lost productivity, worker’s compensation, and insurance costs. Additionally, the direct cost of missing work because of back pain is approximately $20 billion.
On average, how much does back pain cost a sufferer?
Each year, back pain costs the average consumer more than $2,000 which is quite a lot when you think about it.
What are some other costs that result from back pain?
Apart from the mentioned costs, sufferers of back pain are more likely to experience fear about increased costs and the inability to earn money. They also tend to experience social withdrawal, family strain, and disappointment with healthcare facilities and providers.
Additionally, low back pain contributes to global poverty and inequality, since sufferers are unable to earn a living.
International Back Pain Statistics
It’s always a good thing to get a broader idea of back pain and focus on international statistics as well. Here are some of the most interesting global statistics for back pain.
Back Pain Prevalence Rates Worldwide
- In the UK, low back pain is the most common disability in young adults and the main cause for losing more than 100 million workdays annually.
- At the same time, in Sweden, the number of days lost has quadrupled from 7 million to 28 million, although the social compensation systems may be considered responsible for this extreme increase.
- According to the Global Burden of Disease, low back pain is one of the main injuries and diseases, leading to the highest number of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Additionally, the lifetime prevalence of low back pain is expected to be at 60% to 70% in industrialized countries.
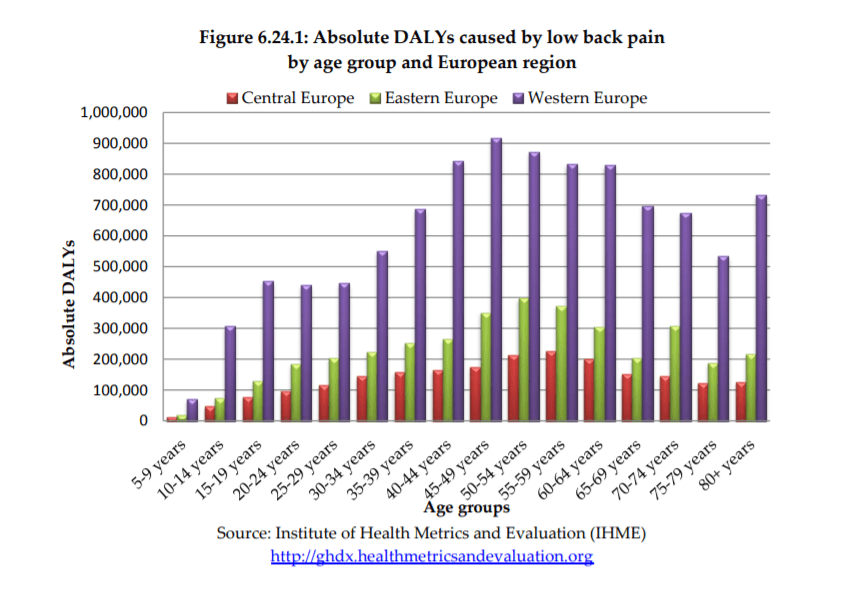
Source: Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation (HME)
- The higher prevalence in women may be due to the higher sensitivity pain, menstrual cycle fluctuations, hormonal changes, menopause, pregnancy, and willingness to report pain.
- At least 540 million people around the world are affected by low back pain.
- In industrialized countries, the second most common cause of DALYs was low back.
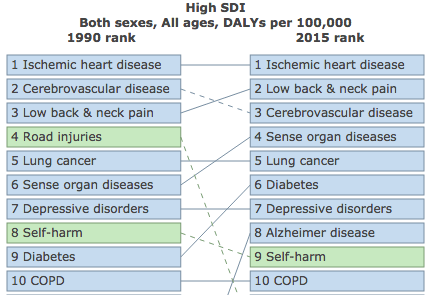
- Age is one of the most important factors in low back pain prevalence, as supported by the higher rates in countries with aging populations. For example, Germany is considered to be one of the ‘’super-aged’’ countries and it’s estimated to have one-third of its population older than 65 by 2050.
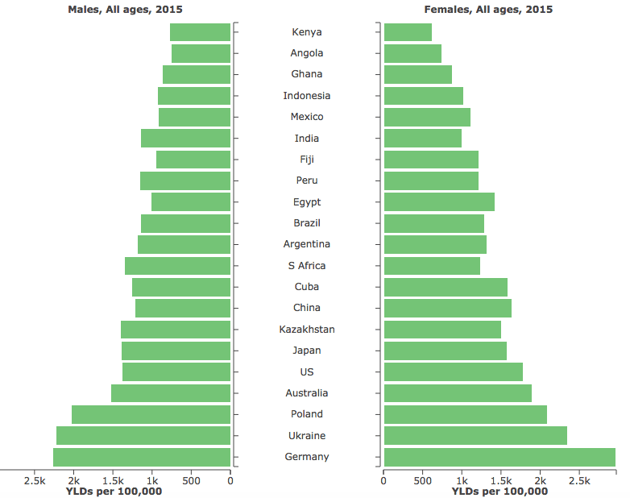
- A research conducted from the University of Queensland’s School of Population Health in Australia has compared the prevalence levels of back pain:
- Western Europe: 15%
- North Africa/Middle East: 14.8%
- North America: 7.7%
- Central America: 6.6%
- Caribbean: 6.5%
Tips to Prevent Back Pain
As you may have noticed already, back pain can result from many things, but most often it’s associated to an everyday activity done incorrectly. Lucky for you, back pain prevention is easy; there are some adjustments that you may have to get used to, but it will be worth it.
Exercise
It goes without saying that exercise is one of the most important things you can do to prevent back pain. Muscles are meant to move, not stay still for a long period of time. If you’re not in good shape, you’re more likely to suffer from back pain even from the simplest movements like bending over to vacuum.
Also, exercise helps to keep your joints fluid and weight down. If you’re overweight, you can add extra strain on your back which leads to back pain.
Ergonomic Chair
If you’re someone who spends your day working in an office or sitting down, you need to invest in a proper ergonomic chair. Nowadays, ergonomic chairs are becoming highly popular and for good reasons. They help align your posture, keep your feet flat on the floor, maintain your neck and head supported at all times, and so much more.
You can find affordable ergonomic chairs for less than $200 and they’re worth every penny. They should be a staple in your home and office if you want to prevent back pain.
Sleep Sideways
Most people enjoy sleeping flat on their backs and if you’re one of them, here’s what we have to say about it. Most researches indicate that the best position for sleeping in sideways. However, if you should sleep on your stomach, it would be best to put a pillow under your lower back as it can alleviate the stress off your back. If you have a supportive mattress and pillow under your head, you’re good to go.
Eat Healthy
This may seem unnecessary, but if you adapt healthy eating habits, not only will you have a healthy weight, but you’re also less likely to put stress on your body.
A proper diet with the necessary nutrients with fruits and vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains will keep your digestive system on track. Conversely, if your diet consists of spicy or fast food, it can strain your nervous system, which leads to back pain problems.
Reduce Stress
Most people don’t realize how much stress actually impacts your back. If you put unnecessary stress on your body, it will cause you to tense your muscles and this constant tension will lead to back pain. You should opt for any activity to help you reduce stress if you want to prevent back pain. Such activities can include meditation, yoga, deep breathing, biofeedback, guided imagery, and tai chi.
The Bottom Line
Back pain is one of the most common injuries and diseases, that’s why you should never delay in seeking treatment. Luckily, there are many treatment alternatives that you can use to relieve your back pain or symptoms at any age.
You should know that you’re never alone in this as the majority of the population has experienced or will experience at least one episode of back pain sometimes in their lives. As you’ve come to learn already, the smallest things can negatively impact your back, but hopefully these back pain statistics will raise awareness about this prevalent problem.
References
- Assessment: Use of epidural steroid injections to treat radicular lumbosacral pain
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000256734.34238.e7
- Dunn KM, Campbell P, Jordan KP. Long-term trajectories of back pain: cohort study with 7-year follow-up. BMJOpen 2013; 3: e003838.
- Global Health Group Data Exchange http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool accessed Nov 15, 2020).
- Hartvingsen J, Hancock MJ, Kongsted A, Louw Q, Ferreira ML, Genevay S, Hoy D, Karppinen J, Glenn Pransky, Sieper J, Smeets RJ, Underwood M. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet 2015; 386: 2145-2191.
- Hoy D, March L, Brooks P, Blyth F, Woolf A, Bain C, Williams G, Smith E, Vos T, Barendregt J, Murray C, Burstein R, Buchbinder R. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014 ;73: 968–974
- https://ghdx.healthdata.org/
- https://handsdownbetter.org/health-and-wellness/back-pain-facts-and-statistics/#:~:text=Back%20pain%20accounts%20for%20more,time%20worker%20in%20the%20country.&text=Experts%20estimate%20that%20up%20to,some%20time%20in%20their%20lives.
- https://handsdownbetter.org/health-and-wellness/back-pain-facts-and-statistics/
- https://n.neurology.org/content/68/10/723.full
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24665116/
- https://thesleepdoctor.com/mattress-information/mattress-types/
- https://uwaterloo.ca/news/news/standing-desks-may-lead-lower-back-pain
- https://www.acatoday.org/news-publications/newsroom/key-facts/#:~:text=There%20are%20more%20than%2070%2C000,1%20and%20be%20state%20licensed.&text=Roughly%20another%203%2C000%20chiropractors%20work%20in%20academic%20and%20management%20roles.
- https://www.ahrq.gov/news/newsroom/ahrq-stats.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db369.htm
- https://www.iasp-pain.org/resources/fact-sheets/the-global-burden-of-low-back-pain/#:~:text=Global%20Burden%20of%20Disease%20studies,one%20day%E2%80%9D%5B1%5D.
- https://www.med.umich.edu/1info/FHP/practiceguides/back/back.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572334/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4456393/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8302339/#:~:text=The%20American%20College%20of%20Physicians,massage%2C%20and%20manual%20spinal%20manipulation.
- https://www.statista.com/topics/4333/back-pain-in-the-us/#:~:text=A%20Statista%20survey%20found%20that,26%20percent%20blamed%20physical%20work.
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/common-causes-of-back-pain-diagnosis-and-treatment-2548504
- Pitcher MH, Von Korff M, Bushnell MC, Porter L. Prevalence and Profile of High-Impact Chronic Pain in the United States. J Pain 2019; 20(2): 146−160.
- Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology Carmel Armon, Charles E. Argoff, Jeffrey Samuels, Misha-Miroslav Backonja Neurology Mar 2007, 68 (10) 723-729;
- Walker BF, Muller R, Grant WD. Low back pain in Australian adults. Prevalence and associated disability. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics 2004; 27(4): 238-244.
- Wu A, March L, Zheng X, Huang J, Wang X, Zhao J, Blyth FM, Smith E, Buchbinder R, Hoy D. Global low back pain prevalence and years lived with disability from 1990 to 2017: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Trans Med 2020; 8(6): 299-313.